MMDS Architecture: –
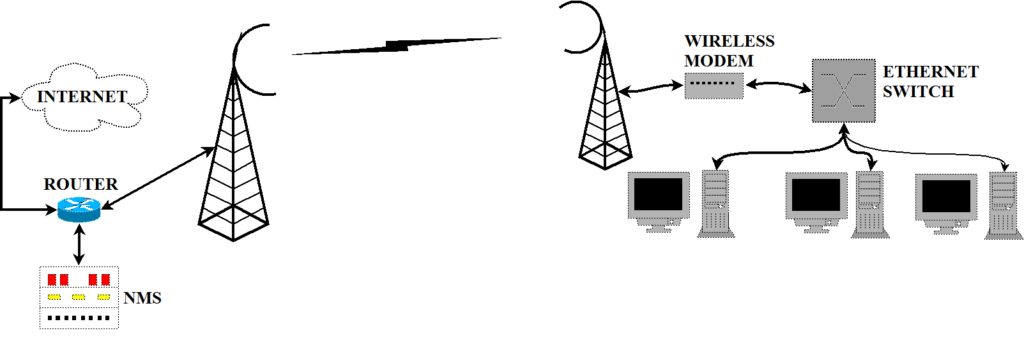
MMDS is also a distribution system which stands for Multichannel/Microwave Multipoint Distribution Service. It is used for small business and home offices. It is not used for large customer requirements such as central offices. It is used where other broadband wireless technologies are difficult to be installed. It uses microwave tower installed on top of the mountains or tall buildings. It covers larger distance compare to LMDS which is about 35 miles.
The above figure depicts MMDS architecture. It consists of Hub equipment and customer side equipments. Hub consists of antenna tower, RF equipments, Modem, Router for connection with internet and network management system (i.e. NMS). Customer side equipments include antenna, wireless modem, Ethernet switch, PCs etc. Hub antenna tower receives wireless signals from multiple users similar to P2MP topology. Each user premise antenna and Hub antenna is connected with P2P microwave link.
Following are the key features of MMDS system:
- It operates in 2.5 GHz and 3.5 GHz frequency bands.
- Hub tower has coverage distance of about 35 miles.
- It uses both P2MP and P2P topologies. P2MP is from multiple users to Hub and P2P is between individual user and Hub.
LMDS Advantages and Disadvantages: –
- Following are the LMDS advantages:
- It has larger bandwidth used for wide variety of applications such as voice, IP, data etc.
• It supports large capacity of users densely populated by sectorizing the area into cells. - Following are the LMDS disadvantages:
- It has high RF equipment costs due to larger number needed.
- Smaller cell size (i.e. 2 to 8 Km) due to requirement of covering large capacity of users.
- Requires many cells to cover larger city areas. This increases installation cost for service providers.
MMDS Advantages and Disadvantages: –
- Following are the MMDS advantages:
- The RF propagation covers 100 Km of region using single antenna tower.
- Due to smaller frequency of use compare to LMDS, MMDS does not suffer from rain attenuation.
- RF equipments are cheaper at lower frequency of 2.5GHz or 3.5 GHz and are available in large quantities.
- Following are the MMDS disadvantages:
- It does not support larger capacity due to lack of sectorization concept in MMDS.
- It suffers from interference from other MMDS and TV applications.
- Large upstream bandwidth needs more and accurate planning.
Thanks to the terrific guide